Industries
Automotive Spare Parts
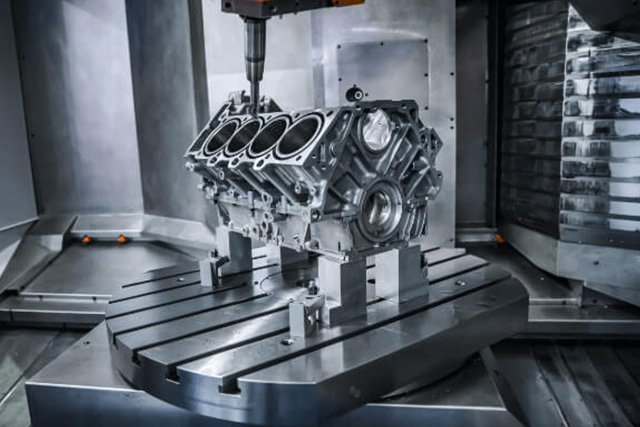

Special Vehicle Spare Parts
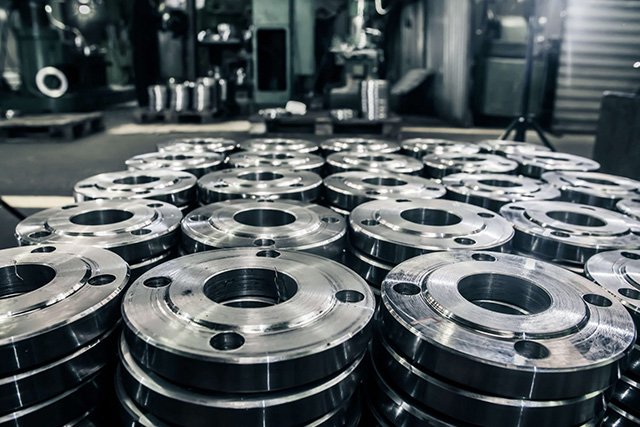

Cutting Tools
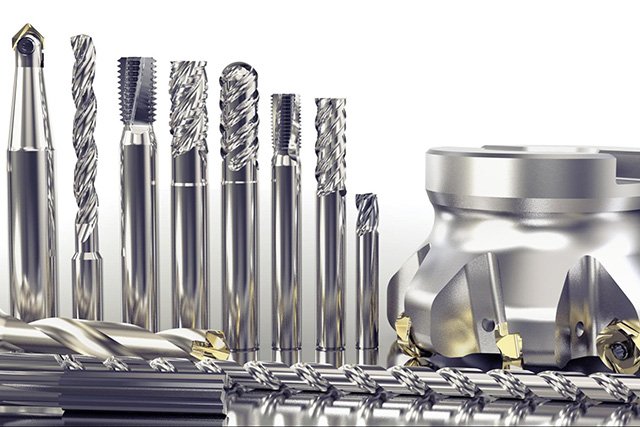

CNC engineering
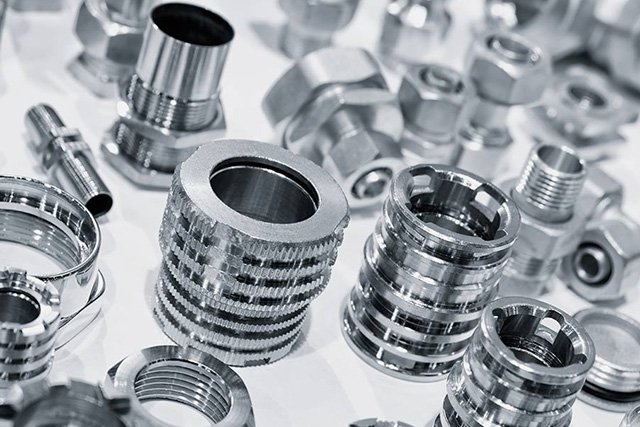

Cabine Manufacturing

Bus Manfuacturing Spare Parts

CNC Machining Materials
The optimal material for selection to apply to a CNC manufacturing application is largely dependent on the particular manufacturing application and its specifications. Most materials can be machined provided that they can withstand the machining process—i.e., have sufficient hardness, tensile strength, shear strength, and chemical and temperature resistance.
(e.g., aluminum, brass, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc.)

(e.g., PEEK, PTFE, nylon, etc.)

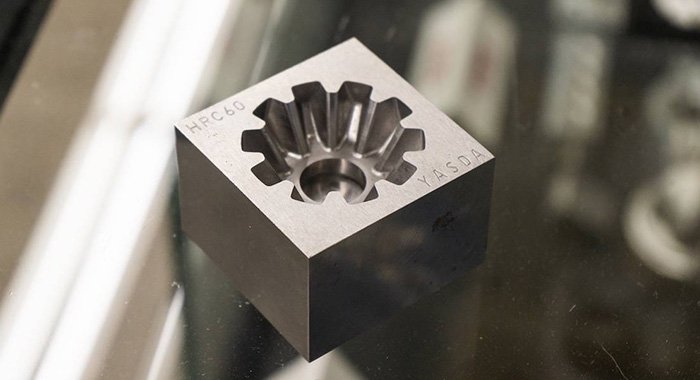
The workpiece material and its physical properties are used to determine the optimal cutting speed, cutting feed rate, and depth of cut. Measured in surface feet per minute, the cutting speed refers to how fast the machine tool cuts into or removes material from the workpiece. The feed rate—measured in inches per minute—is a measure of how fast the workpiece is fed towards the machine tool, and the cut depth is how deep the cutting tool cuts into the workpiece. Typically, the workpiece will first undergo an initial phase in which it is roughly machined to the approximate, custom-designed shape and dimensions, and then undertake a finishing phase in which it experiences slower feed rates and shallower cut depths to achieve its more precise and accurate specifications.






